Конспект курса Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Entrepreneur’s Mindset
Сам курс доступен в Coursera, ниже мои заметки из курса.
Introduction
More or less business average
- Where does innovation come from?
-
R&D Facility
-
Insight (from leader)
-
Partnership (colleagues, partners, clients)
-
Vision (Steve Jobs example)
-
Asking questions
- Status Quo
-
Through iterations
-
Work of other
- Keep your mind open
-
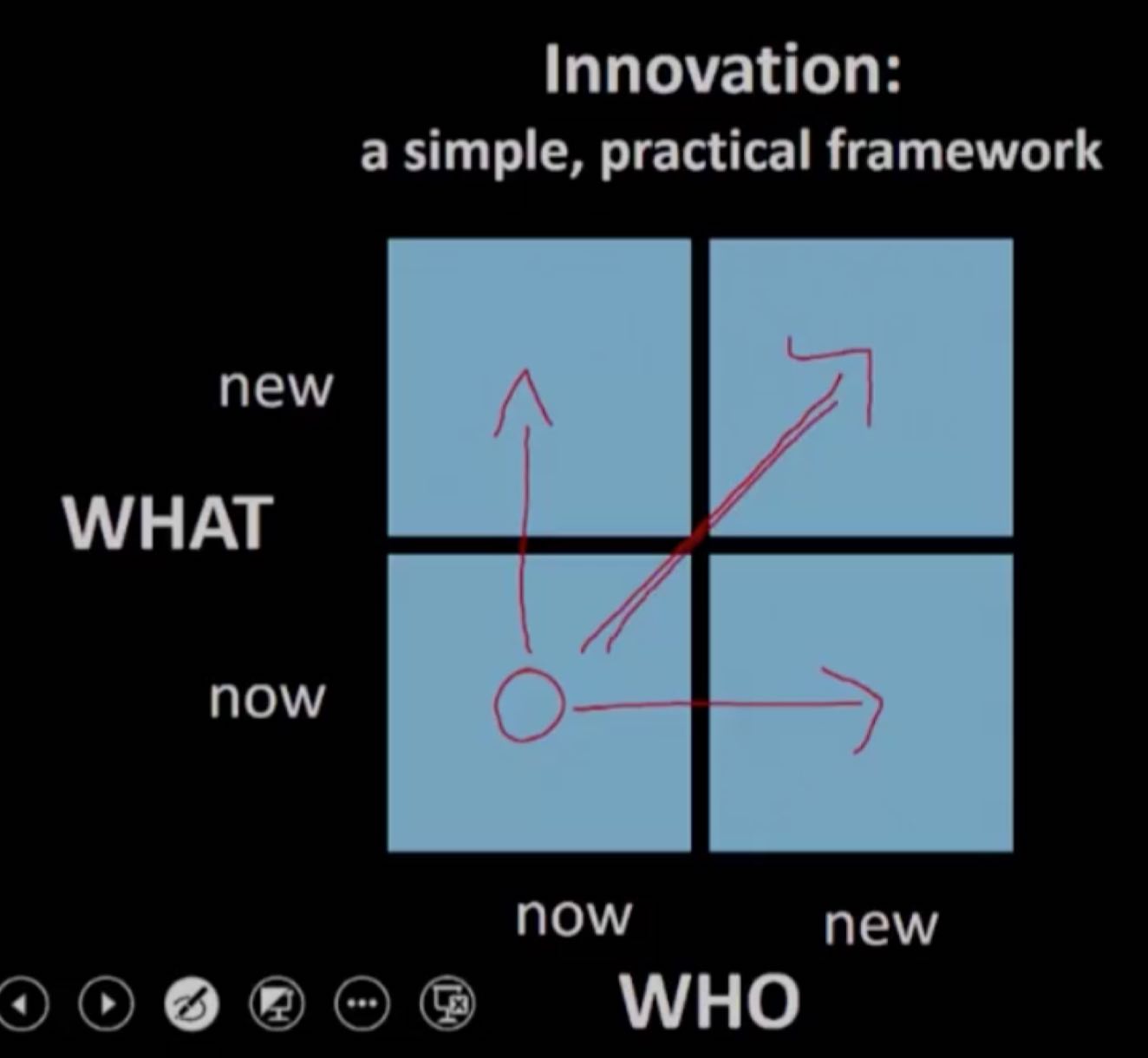
How to drive an innovation
- What product
- Whom to sell
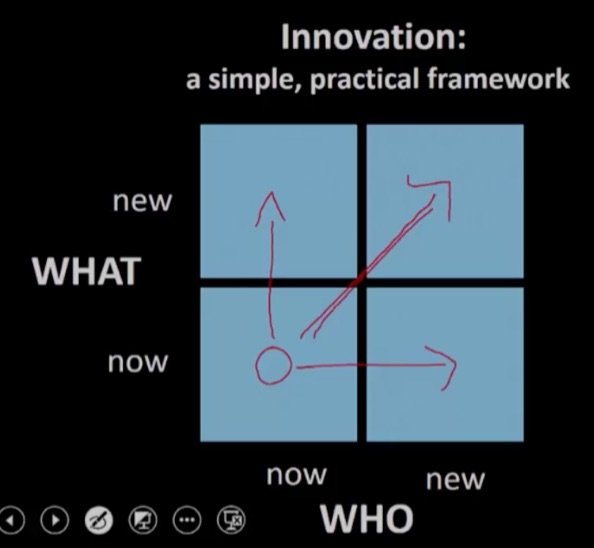
Innovation Portfolio Matrix
Definitions
Innovation
- Developing a new solution or way of doing smthg that drives differentiation and creates measurable value
Enterpreneurship
- Pursuing opportunities - often but not always based on innovation - without regard to the resources directly and currently controlled
Innovation/Invetion/Ideas/Enterpreneurship
- Some of enterpreneurship contains all attributes
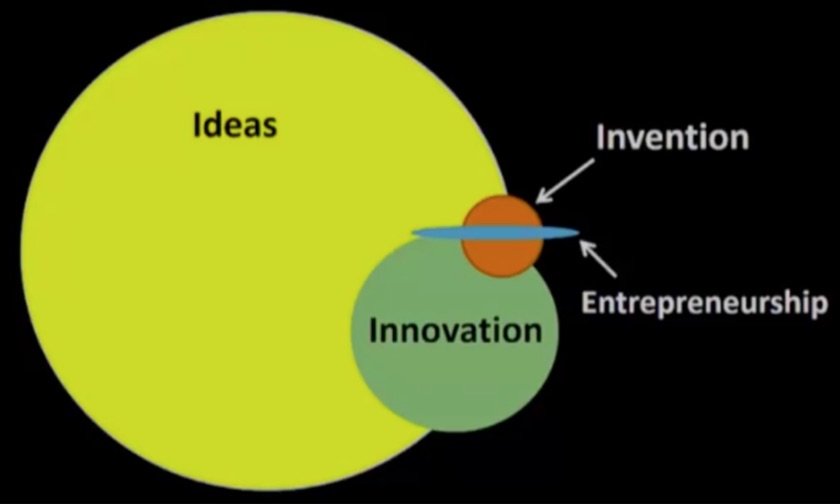
Why innovation so important?
100+ “Unicorns"
Fortune 500 firm
- 1920: 67 years, today: 15 years
Drives growth in companies & economies
Attracts & retains talent
If you don’t innovate, your competitors will
Customer Interviews
Principles
-
People are lying! (people tell us what we want to hear, if you ask the wrong questions)
-
Talk about their life instead of your idea
-
Ask about specifics in the past
-
Listen!
-
Don’t sell!
Right direction (Learn to Launch)
Define
-
Opprortunity
-
Vision & Values
-
Team
Learn
-
Customer Discovery
-
Prototypes
-
Product/Market fit
Launch
-
Products/MVP
-
Biz/Financial Models
-
Organization & Legal
Accelerate
-
Resources: $$ & People
-
Go-to-Market
-
Scale Operations
Entrepreneurial Sets
Toolset
-
Customer Lifecycle
-
Persona
-
Fictional character who represents your target stakeholder
-
name
-
picture
-
demographics
-
-
-
Business Models
- How you make your money with your business?
Skillset
-
Customer Discovery
- Problem to solve
-
Design Thinking & Rapid Prototyping
-
Pricing
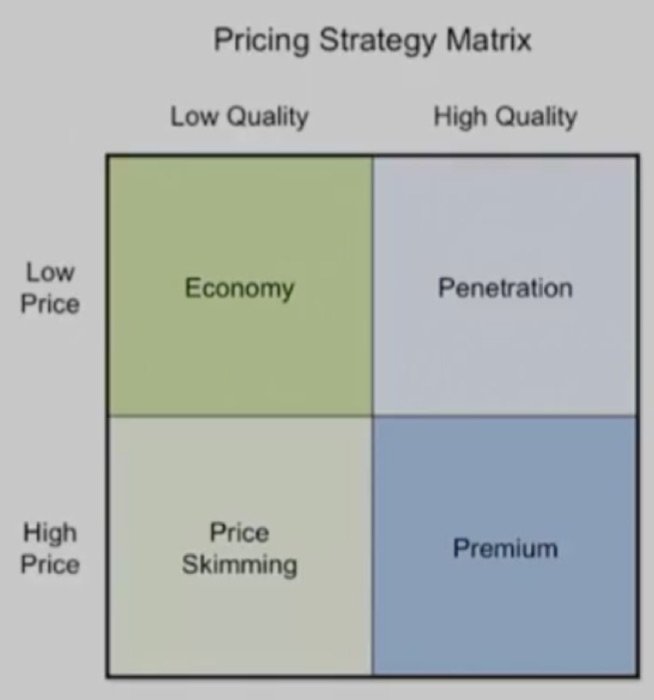
-
Presentation
Mindset
-
10 Traits of Entrepreneur
-
Bias to Action
-
Welcome & Create Change
-
Focus on What Really Matters
-
Optimistic
-
Resourceful
-
Failure-Savvy
-
Resilient
-
Intensely Curious
-
Know your Customer
-
Ask for forgiveness not permissions
-
An entrepreneur is anyone who takes on a task without having all of the resources necessary to accomplish that task available at the outset.
-
-
-
Success rate

-
SNAFU
- situation normal: all fucked up
-
Failure value cycle
-
How to recognize failure ASAP
-
Where failure is not an option? - select this option
-
What is your portfolio of failure zones?
-
Failure is simply an opportunity to begin again. This time, more intelligently. © Henry Ford
-
-
-
Pivoting
-
“Your screw up became my startup…”
- “and my start-up will screw up before it growts up!”
-
Market & Customers
Pivoting must be
-
As you develop an innovative business, now how you can fine tune the market you adress
-
How are you going to address that particular market?
-
Plan an iterations
- For pivoting
Startup
Temporary organization designed to search for a repeatable & scalable business model © Steve Blank, 2012
- Goal of a Startup
- TGDIYCMN (Total global domination in your chosen market niche)
- Advantage
- Speed of learning
- Flexibility in strategy
- Speed of execution
- Common Mistakes
- Full Scale Roll Out
- Webvan example
4.8$ on IPO, but sales only 350k$, and 50$ Mio losses
- Webvan example
- China Syndrome (only for some customers)
- Selling to everyone everywhere
- Breeze
You have to be focus to
- Breeze
- Selling to one customer
- Full Scale Roll Out
1. Market Segmentation
-
What to do?
-
Brainstorming with sticky notes win all potential markets
-
Get market data
-
Communicate with other responsible person to understand your market
-
To find the market segment
-
-
Market segment definition
-
Customers within the market all buy similar products
- repeatable
-
Customers have similar sales cycle and expects products to provide value in similar ways, so sales process is scalable
- scalable
-
There is “word of mouth” between customers in the market, so they can serve as compelling and high-value references for each other in maker
- to get marketing agents
-
2. TAM-SAM-SOM
-
What is it?
-
TAM = Total Addressable Market
- How big at the end can become
-
SAM = Serviceable Addressable Market
- Limited for the next few years
-
SOM = Serviceable Obtainable Market
-
What your market share can be?
-
Realistic
-
-
-
Per segmentation you have different percent of TAM>SAM>SOM
- Choose the
3. Multi-criteria
-
Different criteria - Column
-
Segment
-
- Buyer reason
-
-
Criteria
-
Size of market
-
customers
-
Access to decision making unit (DMU)
-
Innovation speed market
-
Your love for the market
-
MVP potential
-
Customer Pain?
-
-
Innovation curve
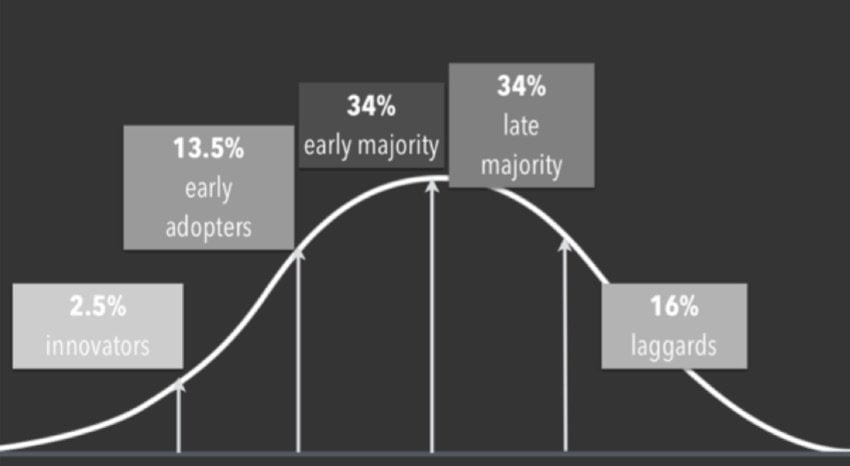
- Innovators (2%)
- Early adopters (14%)
- Early/Late majority (34%)
- Laggards (16%)
-
Beachhead Market
-
Your first entry into the market (TGDIYCMN)
-
Small enough to become a significant player
-
Big enough to generate some cash
-
